In today’s modern and fast world, stress, anxiety, and depression-like mental illnesses have become very common for us, but we don’t know what exactly these are and what the difference is between these problems.
This blog briefly discusses the exact meaning and cause of these mental illnesses and how to reduce these mental illnesses.
Stress, anxiety, and depression definition
- Stress is tension or worry regarding any work; your body naturally reacts when you can not solve your problem.
- Anxiety is a negative emotion like fear and nervousness.
- Depression is a feeling of sadness and loss of interest.

What is stress?
Stress is the feeling of pressure when you can’t handle your work. Normal stress can motivate you, but high stress can give you mental issues.
What are the three types of stress?
1. Acute Stress:
It is a short-term mental condition that can come because of short-term trauma that comes into your life, like worrying about exams, accidents, arguments with loved ones, losing important things, presentations in front of the boss, etc. The time duration of this stress is 3 days to one month.
- Acute stress symptoms:
The symptoms are anxiety, trouble sleeping, avoidance behaviors, fast heart palpitations, problems with breathing, and flashbacks.
- Acute stress treatment:
The solution to this stress is easy: you can meditate, do Prayaram (breathing exercises), do CBT, do physical activities, eat a healthy diet, and talk and connect with others. If you have thoughts about suicide, then take the immediate step of contacting a doctor, and CBT is a very good option.
2. Episodic acute stress:
Episodic acute stress is acute stress that comes back again and again; it is due to work pressure, negative self-talk, financial problems, unhealthy relationships, perfectionist attitudes, high expectations, etc.
The symptoms are anxiety, mood swings, and irritability. Common triggers include work pressure, relationship conflicts, and financial issues. It can be converted into chronic stress if it is not properly treated.
To treat anxiety, try CBT, maintain a healthy lifestyle, break your overthinking with the 4-4-4 rule, exercise regularly, and enjoy activities.

3. Chronic stress:
Chronic stress means a long duration of tension and worries, which occur due to work pressure, traumatic experiences, health issues, old trauma, and unhealthy relationships. Acute stress runs for short periods, but chronic stress keeps the body alert — fight or flight. This stress increases cortisol.
- Chronic stress symptoms:
It gives you so many mental and physical health issues like depression, anxiety, increased blood pressure, heart diseases, hypertension, migraine, headaches, sleeping disorders, irritation, and sexual dysfunction. This stress may include childhood problems or today’s life stress.
- Chronic stress treatment:
The solution is exercise, proper sleep, yoga, meditation, keeping a distance from phones and social media, reducing caffeine and junk food, and avoiding self-isolation. If you ignore this stress, then it can create mental as well as physical issues.
Physical symptoms of stress:
Physical symptoms are headache, body pain, restlessness, digestive issues, muscle tension, fatigue, and changes in appetite or sleep patterns.
How to stop stress?
It is important to manage stress because it can affect emotional, physical, and behavioural health. Self-care is the first step to being safe from stress; good rest, a balanced diet, regular exercise, and relaxation techniques like meditation or yoga can help.
Keep in contact with your friends and relatives. Avoid unhealthy habits, such as alcohol. Think positively, be proactive and grateful, and help others.
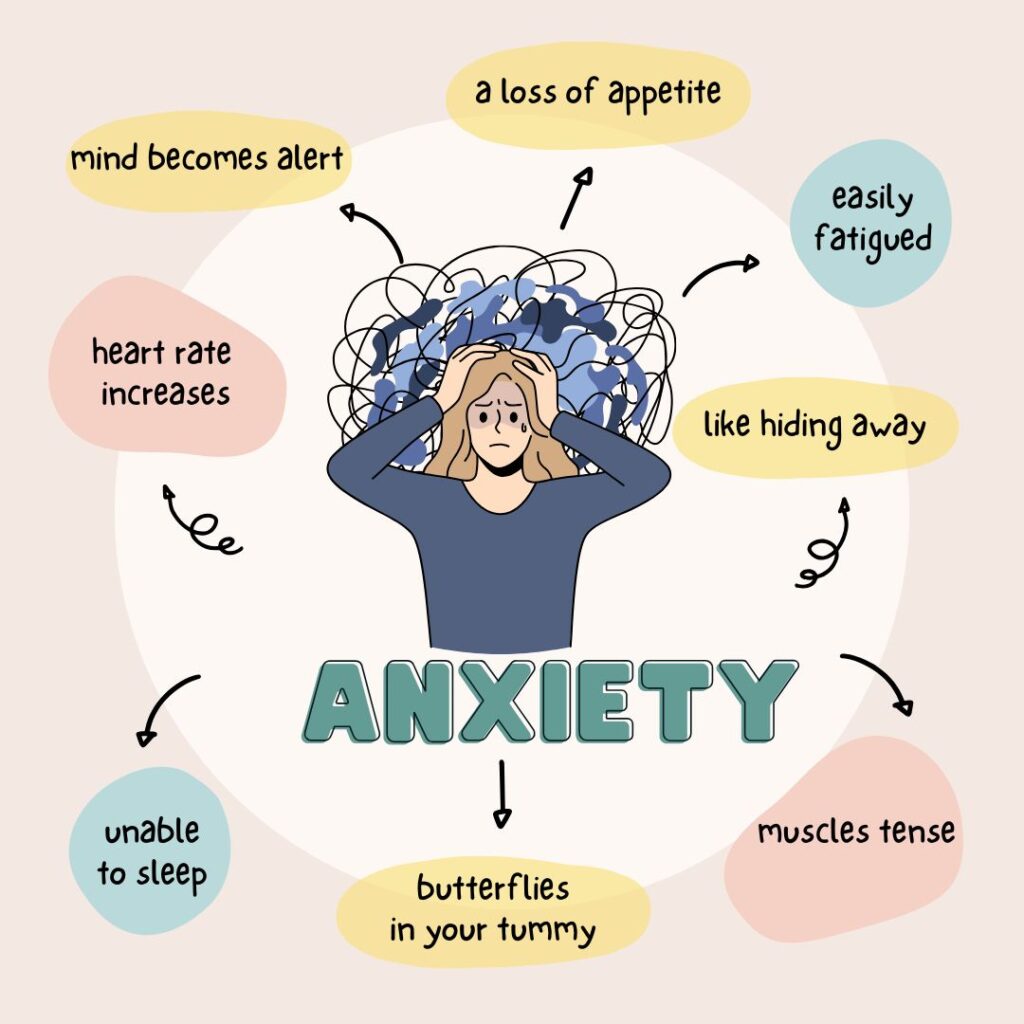
What is anxiety?
Anxiety is a natural response involving fear or worry during stressful or challenging situations. When your body senses a threat or danger, it automatically switches to “fight or flight” mode. Due to that, your heart rate increases, muscles tense, and the mind becomes alert. Little anxiety is normal, like before exams or public speaking. But if it is kept for a long time, then it becomes an anxiety disorder.
What are all the types of anxiety?
1. Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD):
It is a mental health issue in which people feel fear about daily small and uncontrolled things. The signs of this are muscle tension, headache, nausea, grouchiness, and sweating; the patient does not properly concentrate. GAD is connected to genetic, biological, and environmental influences. If any patient is worried for more than 6 months and faces a physical problem, it is diagnosed. If you don’t take treatment on time, then it becomes chronic, so you should seek professional help.
2. Selective mutism:
It is an anxiety disorder where patients feel extreme anxiety while talking to others. Most children face this issue: they speak in familiar environments (school and home) but do not speak in social situations. This problem can also occur with other psychiatric disorders like generalized anxiety disorder. Selective mutism can be treated through cognitive-behavioural therapy, where the patient practices how to face the fear.
3. Separation Anxiety Disorder:
It is a condition in which the patient fears being disconnected from a close attachment figure. This problem affects both children and adults. This illness causes emotional distress and effort to avoid being separated; the patient also faces headaches—treatment like therapy and medication help to manage its symptoms and make daily life better. Do fast to take results fast.
4. Specific phobias:
This means limitless and immeasurable phobias from things or situations– like animals, height, environment phobias, injury, blood, or phobia from any disease. This fear is not a real danger but starts instantly with anxiety or fear. Some people try to avoid these things, which affect their daily life. Symptoms include a rapidly increased heartbeat, sweating, panic attacks, difficulty breathing, and physical symptoms like chest pain, dizziness, and avoidance. This problem mostly affects children and women.
5. Agoraphobia:
It is an anxiety disorder in which people feel unsafe; they can face panic attacks. Genetic, environmental factors, or traumatic events can trigger this problem. Symptoms include fear of losing control, excessive worries, and the patient’s tendency to avoid crowds, public spaces, or homes. Treatment includes cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT), and in some cases, medication with antidepressants is also suggested.
6. Social anxiety disorder (SAD):
In this condition, people feel anxiety and phobia in social situations. The patient runs away from social situations. It can give you so much stress, which affects school, work, and personal relationships. Its symptoms include being judged by others, physical signs like sweating and trembling, and problems interacting with others. Treatment contains psychotherapy, like CBT, and medicines. Instant diagnosis and support are required to solve the problems.
What is a cure for anxiety?
There is no permanent cure for anxiety, but it is a treatable condition. Treatment includes an effective combination of psychotherapy( cognitive behavioural therapy) and medications (antidepressants, anti-anxiety drugs). CBT helps to identify and replace negative thought patterns. Medication helps to manage the signs, but for a long time, therapy is essential. Lifestyle changes like regular exercise, relaxation techniques, proper rest, and stress management also help control anxiety.
What is the 3-3-3 rule for anxiety?
The 3-3-3 rule is a simple trick for calming anxiety. See only 3 things, listen to 3 sounds, share 3 parts of the body. This technique stabilizes your mind in the present situation without any hacks— it also works on children and adults.
What is life like for someone with anxiety?
Life with anxiety is challenging because the patient feels worry and fear, and physical symptoms can impact daily life routines and relationships. The effects of anxiety include problems in concentration, sleep disturbances, and relationship problems. People feel unnecessary worry and fear, and physical symptoms like rapid heartbeat, sweating, and breathing issues accompany them. This mental health condition can be the reason for social isolation, panic attacks, and relationship strain. The performance also fell in schools and workplaces. People who are anxious start to avoid many situations and lose their opportunities. But with the right support and guidelines, it can be treatable.
What is depression?
Depression is a disease that affects people differently depending on their age, gender, or cultural background. Symptoms can be long-lasting: sadness, laziness, less concentration, and understanding yourself as worthless. Its diagnosis is based on 2 weeks till symptoms. Treatment includes CBT, IPT, and medication, which reduces depression symptoms. In addition to these lifestyle changes, self-care and professional help are also important. Treating this problem can be time-consuming, but proper treatment recovery is possible.
What are the 7 causes of depression?
- Genetic Factors – If a family faces depression problems, then the risk is increased.
- Brain Chemistry Imbalance – Changes in neurotransmitters affect moods.
- Hormonal Changes – During pregnancy, thyroid or menopause hormones can be imbalanced.
- Trauma & Stress – The Loss of a close anyone, abuse, or relationship problems can also be the reason for the trigger.
- Personality Traits – Low self-esteem, self-criticism, or overly dependent personality types face this problem.
- Substance Abuse –The use of alcohol and drugs can increase or start the depression.
- Medical Conditions – The impact of chronic illnesses like cancer, diabetes, or heart disease also affects mental health.

What are the 7 types of depression?
- Major Depressive Disorder (MDD): MDD is usually known as clinical depression and involves long-lasting sadness, even patients not taking an interest in favourite things, changes in sleep, hunger and laziness, feeling guilt, and even some patients wanting to end their lives. These things run for more than 2 weeks.
- Persistent Depressive Disorder (PDD): Formerly known as dysthymia, this is chronic depression of approximately 2 years’ duration. It’s not as severe as the MDD, but the duration of the symptoms is a long time, like sadness, irritability, laziness, low self-esteem, and less concentration.
- Bipolar Disorder: Bipolar disorder is a condition of mood swings; the patient feels depressed or has a very high mood. When a patient feels depressed, then its symptoms are the same as MDD- like laziness, improper rest, hopelessness, irritability, and low self-esteem.
- Postpartum Depression (PPD): PPD occurs after childbirth, and it is more severe than “baby blues”. In this, women feel intense sadness and mood swings; it is very hard to make a connection and bond with their baby, they feel anxiety, and sometimes they have thoughts of harm to themselves and the baby. If it is untreated, it can last for over one year.
- Premenstrual Dysphoric Disorder (PMDD) is an intense and more serious type of premenstrual syndrome (PMS). In this patient’s case, mood swings, irritability, extreme laziness, and feelings of hopelessness affect daily life. PMDD is much stronger and more disruptive than PMS.
- Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD): SAD usually happens in the winter when sunlight is very low. In this illness, patients face depression, laziness, weight gain, and more sleep.
- Atypical Depression: This depression is different. The patient desires to eat and sleep more, but it can change your mood after a positive event.
Is depression 100% curable?
- Depression is not 100% curable, but it can be treated with therapy, medication, and lifestyle changes.
- It relapses, so long-term treatment and support are important.
- Every patient has personalized treatment — some want to be treated with meds, some want therapy, and some patients need both.
- Depression is also a chronic condition that can be regularly managed with self-care and monitoring.
- Recovery is a slow process, and patience and a support system are important.
- Recognizing symptoms early, such as low mood, fatigue, and loss of interest, is important.
- With the right treatment and help, people can live their lives purposefully and happily.
- The cure does not mean the perfect end, but living a healthy life with symptoms.
- Support and healing are possible.
Conclusion:
In today’s technology and fast-paced world, stress, anxiety, and depression become very common, but it is important to get treatment on time. Stress can be short-term or chronic. Anxiety is a natural response that can be converted into a disorder; depression is a serious condition that impacts both emotional and physical well-being. These three conditions may not have a permanent cure, but lifestyles can be changed with therapy and medication. The most important thing is to get help, and with proper guidance, you can live a balanced life.
FAQ:
1. What are the 5 warning signs of stress?
- Feel anxious and overwhelmed.
The sensation is like something running in your mind or taking tension every time.
- Irritability or Impatience in small things:
Irritate instantly, become angry, or shout without any reason.
- Fatigue & Low Energy
Feel low energy the whole day, whether the rest is complete.
- Appetite Changes
Some people eat more (stress eating), and some decrease their food.
- Changes in Behavior:
Keep your distance from people, take alcohol/drugs, or do nail bites.
2. What is the Link Between Smoking and Mental Health Conditions?
Smoking and mental health have a deep connection. A patient who suffers from depression, anxiety, or schizophrenia most likely smokes. Taking a cigarette may calm your mind temporarily, but in reality, it increases stress and mental health symptoms. But whenever a person leaves smoking, their moods become better, and anxiety-depression and overall well-being improve— sometimes, it affects antidepressants.
3. What is the difference between anxiety and depression?
Anxiety and depression are both the same mental illnesses, but their symptoms are different. Anxiety patients have much worry, fear, and tension, although depression symptoms are sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest. Both have physical symptoms as well, like laziness and poor concentration. Anxiety patients take future tension, and depressive people do not want to live. Anxiety is filled with “what if” thoughts, and a depressed person thinks, ” What’s the point?”. Both are treated with medication and therapy.
4. What is the depression anxiety stress scale?
The Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Scale (DASS) is a self-report scale that is used to measure depression, anxiety, and stress. It has two versions, DASS-42 and DASS-21. The score increases as severity increases. The Psychology Foundation of Australia makes this scale. This scale measures three emotional states: depression, anxiety, and stress — each with its symptoms.
5. Can anxiety cause chest pain?
Anxiety causes chest pain whenever the body’s stress response activates and hormones are released like adrenaline. This pain makes you feel sharp, aching, or under pressure.